Production is a core concept in economics and business, and understanding its function can offer valuable insights into how goods and services are created and distributed. This article breaks down what production is, why it is important, and how it works in both simple and complex systems.
What Is Production?
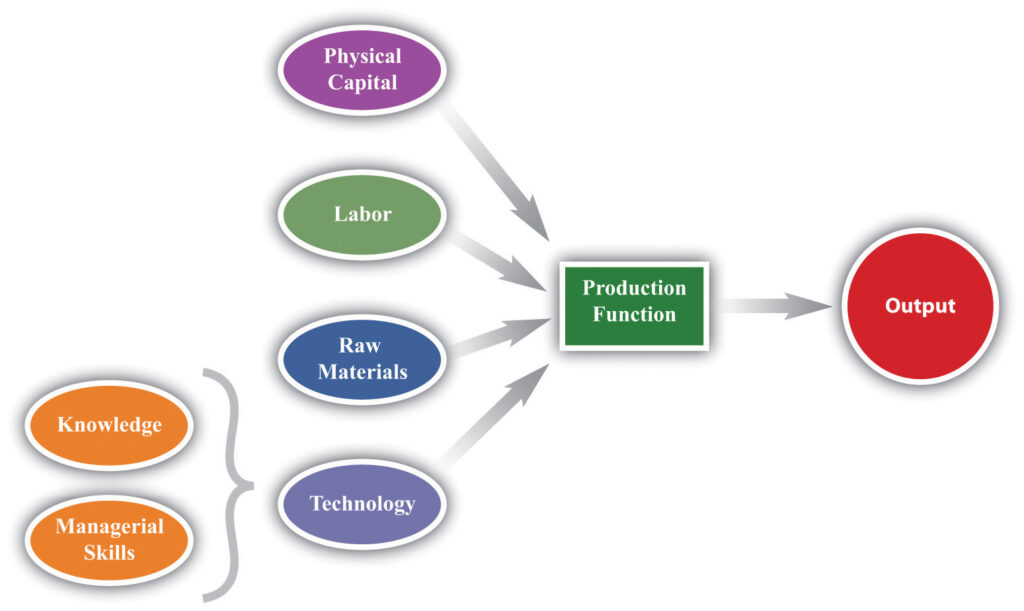
At its most basic level, production is the process of creating goods and services. It involves transforming raw materials into finished products or providing services that meet the needs and wants of consumers. The production process can vary widely depending on the industry, the type of product or service, and the scale of operations.
In essence, production is all about converting inputs—like raw materials, labor, and machinery—into outputs that people can use. This process is crucial because it enables societies to meet their needs and sustain economic activity.
Why Is Production Important?
Production is fundamental for several reasons:
- Economic Growth: Production drives economic growth by creating jobs, generating income, and fostering innovation. As businesses produce more goods and services, they contribute to the overall wealth of a nation.
- Meeting Needs: Through production, societies can fulfill their basic needs, such as food, shelter, and clothing. It also caters to desires, from entertainment to luxury items, improving the quality of life.
- Efficiency and Innovation: The quest to improve production processes leads to innovations in technology and efficiency. This not only makes production more effective but also helps in reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Global Trade: Production allows for trade between nations. Countries can specialize in producing certain goods and exchange them with others, leading to a more diverse range of products available worldwide.
How Does Production Work?
The production process can be divided into several stages, each crucial for converting raw materials into final products or services. Here’s a closer look at these stages:
Input Gathering
The first stage involves gathering all the necessary inputs. These inputs can be categorized into:
- Raw Materials: Basic materials like minerals, agricultural products, and chemicals.
- Labor: The human effort involved in the production process.
- Capital: Machinery, tools, and equipment used in production.
- Entrepreneurship: The skills and initiative required to organize and manage the production process.
Production Planning
Once inputs are gathered, the next step is to plan how they will be used. This involves:
- Designing Production Processes: Determining how to efficiently combine inputs to produce the desired output.
- Scheduling: Organizing the timing of production activities to ensure smooth operations.
- Resource Allocation: Deciding how much of each input is needed and where it should be used.
Production Execution
In this stage, the actual production takes place. Depending on the type of product, this might involve:
- Manufacturing: Using machinery and labor to create physical products.
- Assembly: Putting together various parts to form a final product.
- Service Delivery: Providing services directly to customers, such as in healthcare or education.
Quality Control
Ensuring that the output meets certain standards is crucial. Quality control involves:
- Testing: Checking products for defects or issues.
- Inspection: Reviewing processes and outputs to ensure they meet quality standards.
- Feedback: Gathering information from customers to make improvements.
Distribution
After production, the final products need to be distributed to consumers. This involves:
- Packaging: Preparing products for shipment or sale.
- Logistics: Managing the transportation and delivery of products to retailers or directly to customers.
- Sales: Marketing and selling the products to end-users.
Who Are the Key Players in Production?
Several key players are involved in the production process:
- Producers: The individuals or companies responsible for creating goods or providing services.
- Suppliers: Those who provide the raw materials or components needed for production.
- Consumers: The end-users of the products or services, whose needs and preferences drive production.
- Regulators: Government agencies and organizations that set standards and regulations for production processes.
What Are the Different Types of Production?
Production can be categorized into several types, each suited to different needs and industries:
- Job Production: Producing one item at a time, often custom-made. This is typical in artisan or bespoke industries.
- Batch Production: Creating goods in groups or batches, where each batch goes through a set production process before moving to the next. This is common in food manufacturing.
- Mass Production: Manufacturing large quantities of standardized products, often using assembly lines. This is used in industries like automotive and electronics.
- Continuous Production: Operating around the clock to produce large quantities of products, usually in industries such as chemicals and oil refining.Also read Axis Installation Tool: What You Need to Know
How Does Technology Impact Production?
Technology plays a significant role in modern production by:
- Increasing Efficiency: Automation and advanced machinery streamline production processes, reducing labor costs and increasing output.
- Enhancing Quality: Technology helps in maintaining consistent quality through precise control and monitoring systems.
- Reducing Waste: Advanced techniques and equipment minimize waste and optimize the use of resources.
- Facilitating Innovation: Technology drives innovation in product design and production methods, leading to new products and improved processes.
What Are the Challenges in Production?
While production is essential, it also faces several challenges:
- Cost Management: Balancing production costs with pricing and profitability can be difficult.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Issues such as shortages or delays in raw materials can impact production schedules.
- Environmental Impact: Production processes can have significant environmental consequences, requiring efforts to reduce pollution and resource use.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality in large-scale production can be challenging, especially when scaling up operations.
Conclusion
The function of production is central to creating the goods and services that meet the needs and desires of people. By transforming raw materials and resources into valuable products, production supports economic growth, enhances quality of life, and fosters innovation. Understanding the various aspects of production—from the stages involved to the challenges faced—can provide a clearer picture of how economies and businesses operate.








